
What is SQL injection Attack?
A SQL (Structured Query Language) attack, often referred to as SQL injection, is a type of cybersecurity attack where malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities in an application’s input validation mechanisms to manipulate or inject malicious SQL code into the application’s database. This can lead to unauthorized access, data manipulation, and potentially even data theft.
Example…
Here’s a simplified example of how a SQL injection attack might work:
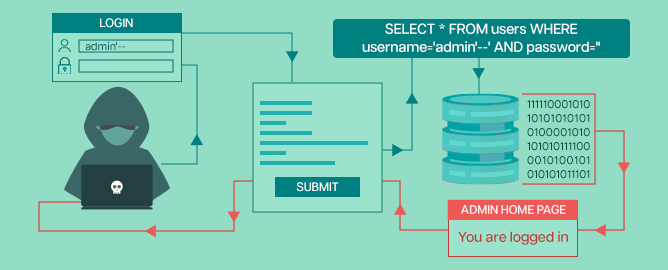
Suppose you have a web application that uses user-provided input to construct SQL queries for database interaction. Let’s say there’s a login page that takes a username and password and constructs an SQL query like this:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '<username>' AND password = '<password>';
If the application doesn’t properly validate or sanitize user input, an attacker could input something like:
Username: ' OR '1'='1 Password: anything
Now, the query becomes:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '' OR '1'='1' AND password = 'anything';
In most cases, '1'='1' is always true, and the attacker would be able to log in without needing a valid username and password. This is just a basic example; SQL injection attacks can be much more sophisticated and damaging.
How to Prevent ?
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Always validate and sanitize user input. Use parameterized queries or prepared statements, which separate the SQL query logic from the user-provided data.
- Escaping User Input: Use proper escaping mechanisms to ensure that user input is treated as data and not executable code.
- Least Privilege: Ensure that the database user account used by the application has the minimum required permissions. This limits the potential damage an attacker could cause even if they successfully inject malicious code.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Implementing a WAF can help detect and block common SQL injection patterns.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Keep your application and database systems up to date with security patches to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Code Reviews and Security Audits: Regularly review your codebase for potential vulnerabilities and perform security audits.
- Application Architecture: Design your application architecture with security in mind. Use authentication and authorization mechanisms effectively, and apply the principle of least privilege.